其它
- MySQL慢查询(sql调优)
- 消息队列(熟悉哪一个,然后细说,使用场景,解决什么问题,实际怎么使用的)
- 多线程
- redis(使用场景,解决什么问题,实际怎么使用的)
- mybatis(一对多 多对一的配置等)
- spring、springboot
- rpc框架
- Git/SVN
- String、StringBuffer与StringBuilder的区别?
Java基础
Overload和Override的区别。Overload的方法是否可以改变返回值的类型?
Overload:重载:同一个类中,方法名相同,参数列表不同。与返回值类型无关。
Override:重写:存在于子父类,或者子父接口中,方法声明相同。
Overload的方法可以改变返回值的类型,因为它与返回值类型无关。
请描述ArrayList和Vector的区别,HashMap和Hashtable的区别。
就ArrayList与Vector主要从二方面来说
- 同步性:Vector是线程安全的,也就是说是同步的,而ArrayList是线程序不安全的,不是同步的
- 数据增长:ArrayList、Vector的初始容量都为10,Vector的加载因子是1,扩容为增加原来的1倍(原来:10;扩容后:20);ArrayList的加载因子为0.5,扩容为增加原来的0.5倍再+1(原来:10;扩容后:16)
HashMap与HashTable主要从三方面来说
线程是否安全: HashMap 是⾮线程安全的,HashTable 是线程安全的;HashTable 内部的⽅法 基本都经过 synchronized 修饰。(如果你要保证线程安全的话就使⽤ ConcurrentHashMap 吧!)
效率: 因为线程安全的问题,HashMap 要⽐ HashTable 效率⾼⼀点。另外,HashTable 基本被淘汰,不要在代码中使⽤它;
对Null key 和Null value的⽀持: HashMap 中,null 可以作为键,这样的键只有⼀个,可以 有⼀个或多个键所对应的值为 null。但是在 HashTable 中 put 进的键值只要有⼀个 null, 直接抛出 NullPointerException
初始容量⼤⼩和每次扩充容量⼤⼩的不同 :
①创建时如果不指定容量初始值,Hashtable 默认 的初始⼤⼩为11,之后每次扩充,容量变为原来的2n+1。HashMap 默认的初始化⼤⼩为16。之后 每次扩充,容量变为原来的2倍
②创建时如果给定了容量初始值,那么 Hashtable 会直接使⽤ 你给定的⼤⼩,⽽ HashMap 会将其扩充为2的幂次⽅⼤⼩。也就是说 HashMap 总是使⽤2的幂作为哈希表的⼤⼩,后⾯会介 绍到为什么是2的幂次⽅
底层数据结构: JDK1.8 以后的 HashMap 在解决哈希冲突时有了较⼤的变化,当链表⻓度⼤于 阈值(默认为8)时,将链表转化为红⿊树,以减少搜索时间。Hashtable 没有这样的机制
java中实现多态的机制是什么?
所谓多态就是指程序中定义的引用变量所指向的具体类型和通过该引用变量发出的方法调用在编程时并不确定,而是在程序运行期间才确定,即一个引用变量倒底会指向哪个类的实例对象,该引用变量发出的方法调用到底是哪个类中实现的方法,必须在由程序运行期间才能决定。因为在程序运行时才确定具体的类,这样,不用修改源程序代码,就可以让引用变量绑定到各种不同的类实现上,从而导致该引用调用的具体方法随之改变,即不修改程序代码就可以改变程序运行时所绑定的具体代码,让程序可以选择多个运行状态,这就是多态性。
多态分为编译时多态和运行时多态。其中编辑时多态是静态的,主要是指方法的重载,它是根据参数列表的不同来区分不同的函数,通过编辑之后会变成两个不同的函数,在运行时谈不上多态。而运行时多态是动态的,它是通过动态绑定来实现的,也就是我们所说的多态性。
同步和异步有何异同,在什么情况下分别使用他们?举例说明
同步是发送一个请求,等待返回,然后在发送一个请求。异步是发送一个请求,不用等待,随时可发送下一个请求
如果数据将在线程间共享。例如正在写的数据以后可能被另一个线程读到,或者正在读的数据可能已经被另一个线程写过了,那么这些数据就是共享数据,必须进行同步存取。 当应用程序在对象上调用了一个需要花费很长时间来执行的方法,并且不希望让程序等待方法的返回时,就应该使用异步编程,在很多情况下采用异步途径往往更有效率。 同步是安全的,异步是不安全的
5
Java算法
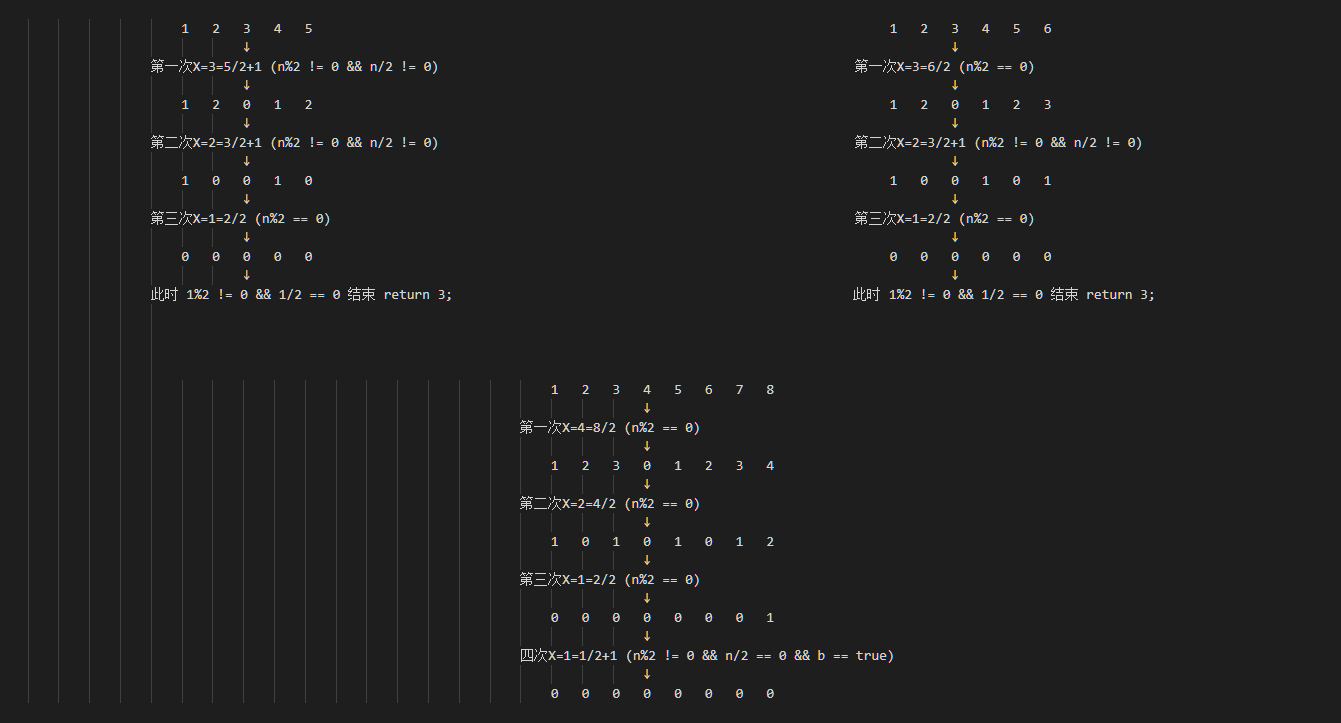
有N个篮子(分别编号为1~N),第i个篮子里有i个苹果;取一个整数X,篮子标号大于等于X的篮子都取出X个苹果(小于X的篮子不动);请用Java编码实现输入N,最少取多少次X(每次的X可以不同)可以将每一个篮子清空?
注:以下只是我自己的解法,不能保证100%准确,欢迎指正
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33public class Tesst {
// 记录X的次数
static int count = -1;
// 整个遍历过程全部满足n%2 == 0(除了最后一次)
static boolean b = true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(get(4));
}
public static int get(int n) {
if (count == -1 && n == 1) {
return 1;
}
if (n%2 == 0) {
count++;
get(n/2);
return count;
} else {
if (n/2 == 0) {
if (b) {
count++;
}
count++;
return count;
} else {
b = false;
count++;
get(n/2 + 1);
return count;
}
}
}
}详解如下:
不用字符串处理函数,实现以单词为单位的逆序
例如:从控制台输入 hello word
输出: word hello1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48package com.liang.utils;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
/**
* @author 马亮南生
* @date 2020-11-24 14:17
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用数组的弊端是只能创建固定大小空间的数组,不灵活
String[] strings = new String[10];
char[] chars = new char[20];
int i, j = 0, k = 0;
// 最后得到的目标字符串
StringBuilder dest = new StringBuilder();
BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
try {
// char(10)表示换行 char(13)表示回车 必须两个一起判断
while ((i = in.read()) != 10 && i != 13) {
if ((char) i != ' ') {
chars[j] = (char) i;
j++;
} else {
strings[k] = new String(chars).trim() + " ";
k++;
chars = new char[20];
j = 0;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 回车后最后一单词未能放入字符串数组
if (j != 0) {
strings[k] = new String(chars).trim() + " ";
}
// 字符串数组从尾迭代将非空字符串加到目标字符串
for (j = strings.length - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (strings[j] != null) {
dest.append(strings[j]);
}
}
System.out.println("逆序后的字符串:");
System.out.println(dest);
}
}编程实现冒泡排序算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42package com.liang.utils;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author 马亮南生
* @date 2020-11-24 14:17
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = new int[10];
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
a[i] = rand.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
printArr(a);
// 冒泡排序
bubbleSort(a);
printArr(a);
}
public static void printArr(int[] a) {
for (int value : a) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] a) {
int temp;
for (int i = a.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) {
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j + 1];
a[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("冒泡排序完成");
}
}请使用 File、FileReader、FileWriter、BufferedReader 和BufferedWriter类,编写一个java 应用程序实现文件的复制
- 文件名自定义;
- 程序可能抛出FileNotFoundException、IOException,需进行处理;
- 所要求的类必须都使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39package com.liang.utils;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author 马亮南生
* @date 2020-11-24 14:17
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
copy("D:/aa.txt", "D:/aa/bb.txt");
}
public static void copy(String oldFileName, String newFileName) {
try {
File file = new File(newFileName.substring(0, newFileName.lastIndexOf("/")));
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
// 字符流拷贝
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(oldFileName));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(newFileName));
String str;
while ((str = reader.readLine()) != null) {
writer.write(str);
writer.newLine();
}
reader.close();
writer.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}5
